What is Casting?
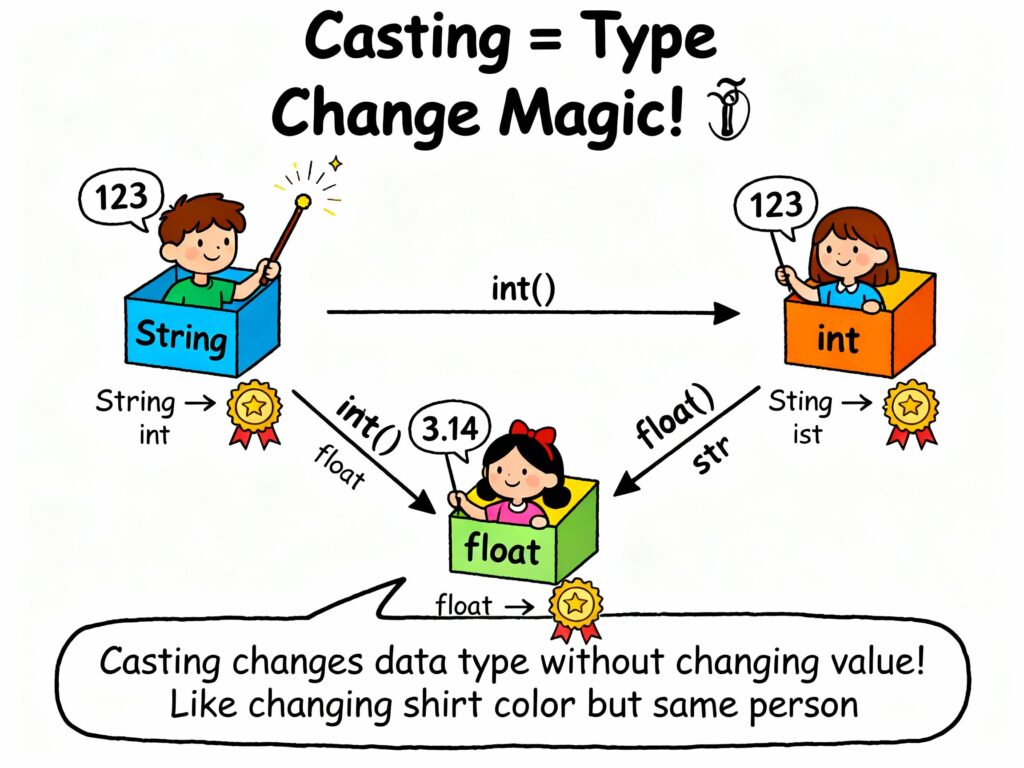
Python casting is the process that we can use for converting one data type value into another. Sometimes we need a value in a specific format, for example, converting a string into a number so we can perform calculations.
Python provides built-in functions to do this easily:
- int() → converts to integer
- float() → converts to float
- str() → converts to string
These type conversions are called casting.
Why Casting Is Needed In Programming?
Casting is most important in Python because we are performing multiple operations in our program, and different operations require values in a specific format. If the data does not match the right type, the program cannot perform the task correctly
Here, we describes multiple points when to use casting:
1) We need to perform math on values that are currently strings.
Sometimes a number is stored as a string, so Python will consider it as text. We cannot add, subtract, or multiply text.
Let’s understand a simple example: If “10” is a string, you can’t do math with it until you convert it to an integer. It means casting converts text-based numbers into real numeric types, allowing calculations to occur.
2) You want to combine or compare values of the same type.
Some operations require same type values. For example, comparing “5” (string) with 5 (integer) won’t work correctly. So the casting ensures both values are in the same data format so the comparison is meaningful.
3) When we are working with user input, which always comes as a string.
Whenever Python takes input from the user (like keyboard, form, or terminal), it stores that value as a string, even if the user typed a number.
For this situation, casting is required to convert that string into an integer, float, or another type before using it.
Types of Casting in Python
Python supports the following types of casting:
- Implicit Casting
- Explicit Casting
Let’s explore each of these in detail.
1. Implicit Casting
Implicit casting means Python itself decides to change the type of a value and automatically converts a data type into another without you having to write anything extra.
Sometimes a mistake happens when converting a smaller or less detailed type into a bigger or more detailed type. So, Python helps to avoid these mistakes or data loss.
First, Python checks two values; if one has more precision (like a float) and the other has less (like an int), Python automatically upgrades the smaller one so both match easily.
What Is Precision In Python?
Precision means how detailed or accurate a number can be stored in memory. If we have a more precise data type, we can predict more exact digits.
For example:
- 5 → no decimal → low precision
- 5.123456 → many digits → high precision
You can see, the float has higher precision because it has a more accurate number.
Example of Implicit Casting:
# Implicit casting from int to float
num_int = 20
num_float = num_int + 5.6
print(num_float)
Output:
25.6
In the above example, Python automatically converts the integer num_int into a float to perform the addition with a float value.
2. Explicit Casting
Explicit casting means you manually tell Python to convert one data type into another by using a specific function. The difference is that Python will not do it automatically; you must give the command yourself.
The explicit casting used multiple functions, such as:
- int()
- float()
- str()
- complex()
- bool()
1) int() Function
int() is a Python function that changes a value into an integer. You can use this function on numbers and strings, but the value should be something effectively turned into a whole number.
Let’s understand in simple words:
- If you give int() a float → Python removes the decimal part.
- If you give int() a string → the string must contain digits only.
- If the value cannot be converted → Python shows an error.
Simple Examples:
1) Converting Float to Integer
price = 15.87
whole_price = int(price)
print(whole_price)
# Output: 15
- Here, Python drops the decimal .87 and keeps only the whole number.
2) Converting String to Integer
value = "456"
number = int(value)
print(number)
# Output: 456
- You can see, “456” is a proper number inside quotes; Python converts it easily.
3) If the String Is Not a Proper Number
num = "42kg"
print(int(num))
# This will give an error because "42kg" contains letters, so the Python won't convert it.
2) float() Function
float() is a built-in Python function that converts a value into a floating-point number. You can also use this function on integers and strings, but the value must look like a valid decimal number.
If you give float() an integer the Python adds .0 at the end, and if you give float() a string, the string must contain a valid decimal number like “44.5” or “99”.
If the text contains letters or symbols, the conversion will fail.
Examples of float():
1) Convert Integer to Float
count = 8
decimal_count = float(count)
print(decimal_count)
# Output: 8.0
- Python simply adds a decimal part because floats always include a fraction.
2) Convert String to Float
marks = "92.4"
score = float(marks)
print(score)
# Output: 92.4
- Since “92.4” is a proper decimal value, Python converts it smoothly.
3) Invalid String Example
data = "12kg"
print(float(data))
# This will cause an error
- “12kg” is not a valid number, so Python cannot convert it.
3) str() Function
str() is a Python function that changes any value into a string (text form). It is only used when you want to combine numbers with text or show the value to the user in a readable format. So str() basically turns data into text that you can display or print.
Examples of str():
#converting Integer to String
age = 21
age_text = str(age)
print(age_text) # Output: '21'
print(type(age_text)) # Output: <class 'str'>
#converting Float to String
temperature = 28.6
temp_text = str(temperature)
print(temp_text) # Output: '28.6'
- The float is also converted into text from with quotes.
4) complex() Function
The complex() function converts numbers or strings into complex numbers, with the format a + bj.
Examples of complex():
count = 8
c_number = complex(count)
print(c_number)
# Output: (8+0j)
- Here, Python places the integer in the real part and sets the imaginary to 0j.
What is the Complex() in Python?
What are the Functions in Python?
What are the Numbers in Python?
5) bool() Function
The bool() function converts a value into a Boolean (True or False). Python checks the value and decides the result if the value is “empty” or “non-empty”.
Examples of bool():
# Integer to boolean
num = 10
print(bool(num)) # Output: True
# String to boolean
text = ""
print(bool(text)) # Output: False
- Any number other than 0 becomes True, and Zero is treated as “nothing”, so the result is False.
- The same rule applied to the String. For example:
msg = ""
print(bool(msg)) # Output: False
msg = "Hello"
print(bool(msg)) # Output: True
Type Conversion for Collections
In Python, we can also convert one collection type into another.
Collections are the groups data like:
Type conversion allows you to change the structure of data. For example, you can change a list into a tuple, or a tuple into a list.
Examples of Collections:
1) Convert List to Tuple
numbers_list = [2, 4, 6]
numbers_tuple = tuple(numbers_list)
print(numbers_tuple) # Output: (2, 4, 6)
#here, the items stay the same; only the container changes.
2) Convert Tuple to List
points_tuple = (10, 20, 30)
points_list = list(points_tuple)
print(points_list) # Output: [10, 20, 30]
#Now you can modify, add, or remove items because it become a list.
3) Convert List to Set
values = [1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3]
unique_values = set(values)
print(unique_values) # Output: {1, 2, 3}
#This is useful for removing duplicates items
Common Errors in Casting
When you convert one type into another, sometimes Python cannot perform the conversion correctly. Lets’ understand which types of problems we can faces.
1) Invalid Format Strings: This error happens when the string does not look like a number, but you try to convert it into one. Example:
num = "abc"
int_num = int(num) # ValueError
- “abc” is made of letters, not digits. because Python cannot change letters into a number, it shows an error.
2) Precision Loss: When you convert a float to an int, Python removes the decimal part.
value = 7.9
print(int(value))
# Output: 7
# The .9 is removed completely
3) Unsupported Conversions: Some conversions are not possible directly.
int("1.5")
# Not allowed
# "1.5" is a float-like string, not an integer string.

M.Sc. (Information Technology). I explain AI, AGI, Programming and future technologies in simple language. Founder of BoxOfLearn.com.
