What Is a While Loop?
Loop is an essential concept in programming because it prevents writing the same code multiple times.
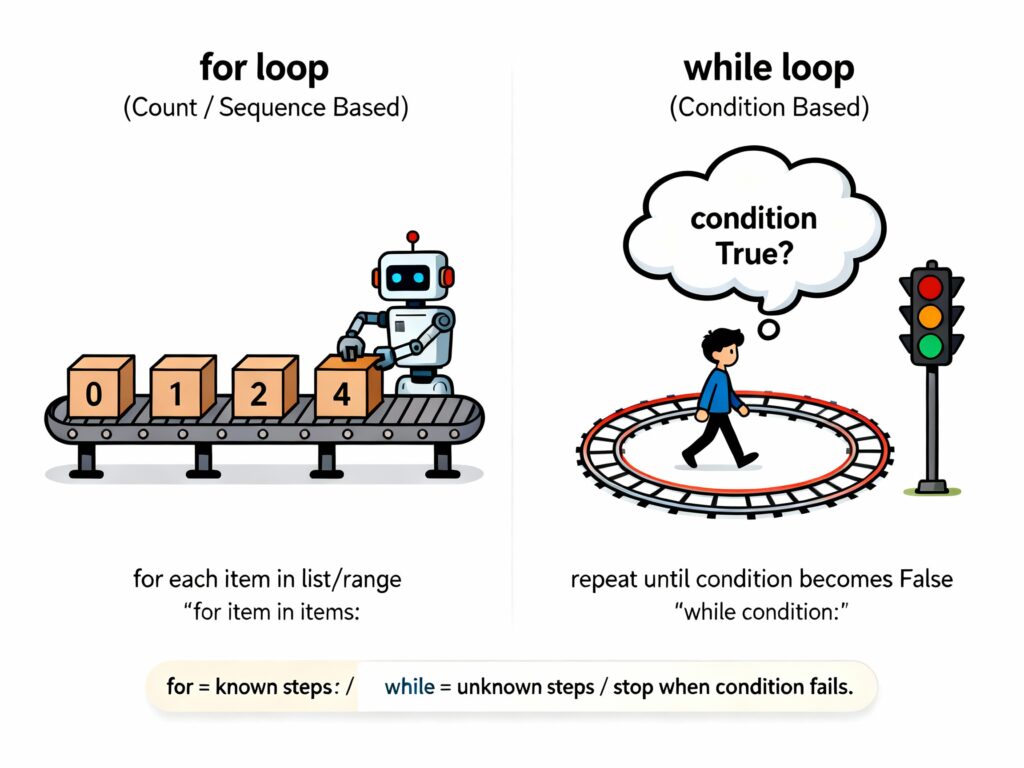
A while loop in Python is used when you want to repeat a block of code again and again as long as a certain condition remains true.
Why Use While Loops In Python?
- A while loop is extremely useful when our program repeats one action multiple times, but we don’t exactly know how many repetitions are required.
- For loops work with a fixed range of actions, but a while loop keeps running as long as the condition stays True.
1) When You Don’t Know the Exact Number of Repetitions
Sometimes, we can’t decide the number of loop iterations in advance. Instead, the loop decides when the program should be closed.
For example: Where we use while loop in real-life projects
- Keep asking a user for valid input until they give the correct value
- Reduce a battery level until it reaches zero
- Wait for a sensor to reach a safe value
2) Dynamic Exit Conditions
- A while loop continues executing until a changing condition becomes False.
- The condition can depend on user input, live data, and more.
3) Real-Time Processes
While loops process a real-time works like:
- Counting down
- Checking a file or connection status
- Validating passwords or numbers
- Reading data step-by-step
While Loop Syntax In Python
while condition:
# statements that keep running while the condition is True
Explanations of the syntax:
1) condition
- The condition is a statement that Python checks before the loop cycle.
- If the condition is True, the loop continues running.
- If it becomes False, the loop immediately stops.
2) Indentation
- Indentation is important in Python because it decides which code belongs inside the loop. For example:
while steps < 3:
print("Taking a step…") # This is inside the loop
while steps < 3:
print("Taking a step…") # This is outside the loop
While Loop Example In Python
Example: Basic While Loop
Let’s write a program that starts counting from 1 and stops when the counter reaches 4.
number = 1 # starting point
while number < 5: # loop runs while this condition is True
print("Current number:", number)
number += 1 # increasing the value so the loop doesn’t run forever
Output:
Current number: 1
Current number: 2
Current number: 3
Current number: 4
While Loops Example With an Else Statement
We can also attach an else block to a while loop. The else part runs when the loop finishes normally, which means the loop condition becomes False, and the loop did not exit using a break statement.
Example: Counting Down a Timer
timer = 4 # starting countdown
while timer > 0:
print("Seconds left:", timer)
timer -= 1
else:
print("Countdown completed successfully!")
Output:
Seconds left: 4
Seconds left: 3
Seconds left: 2
Seconds left: 1
Countdown completed successfully!
Common Operations in While Loops
While loop has multiple different types, such as:
- Infinite Loop
- Break statement
- Continue statement
1. Infinite Loop
- A while loop becomes infinite when its condition never turns False.
- In real projects, we use these loops for menus, chat systems, continuously reading user input, and more.
- But every infinite loop should have a safe exit option; otherwise, your program will run endlessly.
Example of Infinite Loop:
while True:
command = input("Say 'stop' to end the program: ")
if command.strip().lower() == "stop":
print("Program stopped by the user.")
break
2. Break Statement
- The break statement allows us to leave the loop immediately, even if the loop condition is still True.
- We will use the break keyword when a specific condition is met, and we no longer need to continue looping.
Example with Break Statement:
score = 0
while score < 15:
print("Current score:", score)
score += 3
if score >= 9:
print("Stopping early because score crossed 9.")
break
3. Continue Statement:
- The continue keyword skips the remaining code in the current loop iteration and jumps directly to the next iteration.
- This method is useful when we want to ignore certain cases without breaking the whole loop.
Example with Continue Statement:
number = 0
while number < 6:
number += 1
if number % 2 == 0: # skip even numbers
print("Skipping even number:", number)
continue
print("Processing odd number:", number)
Output:
Processing odd number: 1
Skipping even number: 2
Processing odd number: 3
Skipping even number: 4
Processing odd number: 5
Skipping even number: 6
Where We Use a While Loop In Real Projects?
a) Real-Time Sensor Monitoring (IoT Projects)
Imagine you are reading data from a sensor like temperature, humidity, light level, etc. You don’t know how many times the sensor will send readings; you just keep checking until the user stops the system.
For example:
# Keep reading a sensor value until user stops the system
sensor_value = 25 # starting reading (assume)
command = ""
while command != "stop":
print("Current Sensor Reading:", sensor_value)
sensor_value += 1 # just simulating change
command = input("Type 'stop' to end monitoring: ").lower()
print("Monitoring stopped.")
- We used a while loop because we don’t know how long the monitoring should run.
b) Login System With Limited Attempts
In real apps, you don’t know how many times the user will try to log in, but you want to stop after a maximum retry attempts.
Example code:
# Login attempt system with limited tries
correct_pin = "4567"
attempts = 3
while attempts > 0:
pin = input("Enter ATM PIN: ")
if pin == correct_pin:
print("Login successful!")
break
attempts -= 1
print("Wrong PIN. Attempts left:", attempts)
if attempts == 0:
print("Your card is temporarily locked.")
- This code runs until a correct PIN OR attempts run out.
c) Auto-Save Process in a Writing App
Many apps keep saving the user’s work every few seconds until the user closes the app. For example:
# Autosave simulation until user exits
is_editing = True
save_count = 0
while is_editing:
print("Auto-saving draft... (Save no:", save_count, ")")
save_count += 1
action = input("Type 'quit' to close the editor: ")
if action.lower() == "quit":
is_editing = False
print("Editor closed and draft saved.")
d) Game Loop
You all know that games keep running until the player quits or loses. Let’s see the example:
# Simple game loop simulation
player_health = 10
while player_health > 0:
print("Player Health:", player_health)
player_health -= 2
print("Game Over!")
- This game will only stop when the player’s health becomes 0.
Best Practices for Using While Loops
- Set Clear Exit Conditions: You must clearly define when the loop should stop. If the stop condition is unclear or incorrect, the loop may continue forever.
- Minimize Infinite Loops: Infinite loops continue running unless a break statement is used. They are helpful only in very specific situations, like running background tasks or waiting for user commands.
- Validate Input: Users may enter unexpected or invalid data, so your loop should be prepared for anything.
- What is type casting in Python?
- What are numbers in Python?
- How we can use data types in Python?
- What are variables in Python?
- What are strings in Python?

M.Sc. (Information Technology). I explain AI, AGI, Programming and future technologies in simple language. Founder of BoxOfLearn.com.
